Top Picks: Best Remote SSH For IoT (2024) - Secure Access!
Why does the ability to securely access and manage Internet of Things (IoT) devices remotely remain a critical, yet often overlooked, cornerstone of modern technological infrastructure? The power to control, troubleshoot, and update these devices from anywhere in the world, without physical presence, is not just a convenience; it's a fundamental necessity for efficiency, security, and scalability in an increasingly interconnected world. This is the essence of "best remote SSH IoT," a concept that unlocks the full potential of the IoT revolution.
The integration of SSH (Secure Shell) into the IoT landscape offers a robust, secure channel for remote access, allowing administrators and developers to interact with devices as if they were directly connected. This is particularly crucial when considering the distributed nature of many IoT deployments, spanning vast geographical areas or operating in challenging environments. Furthermore, as the number of IoT devices continues to explode, the need for centralized management and control becomes paramount. SSH provides a reliable and standardized method to address these challenges, ensuring that devices can be managed and maintained proactively, minimizing downtime and maximizing operational effectiveness.
The core benefit of utilizing remote SSH access within an IoT environment lies in its capacity to streamline troubleshooting. When an issue arises with a device be it a sensor malfunctioning, a software glitch, or a connectivity problem remote access allows technicians to diagnose and rectify the problem quickly and efficiently. Instead of dispatching personnel to the physical location, which can be costly and time-consuming, administrators can log in securely and analyze the device's logs, configure settings, and even remotely execute commands to resolve the issue. This proactive approach significantly reduces the time it takes to resolve problems and prevents disruptions to critical services. Beyond basic troubleshooting, remote SSH also empowers developers to perform software updates and patch security vulnerabilities.
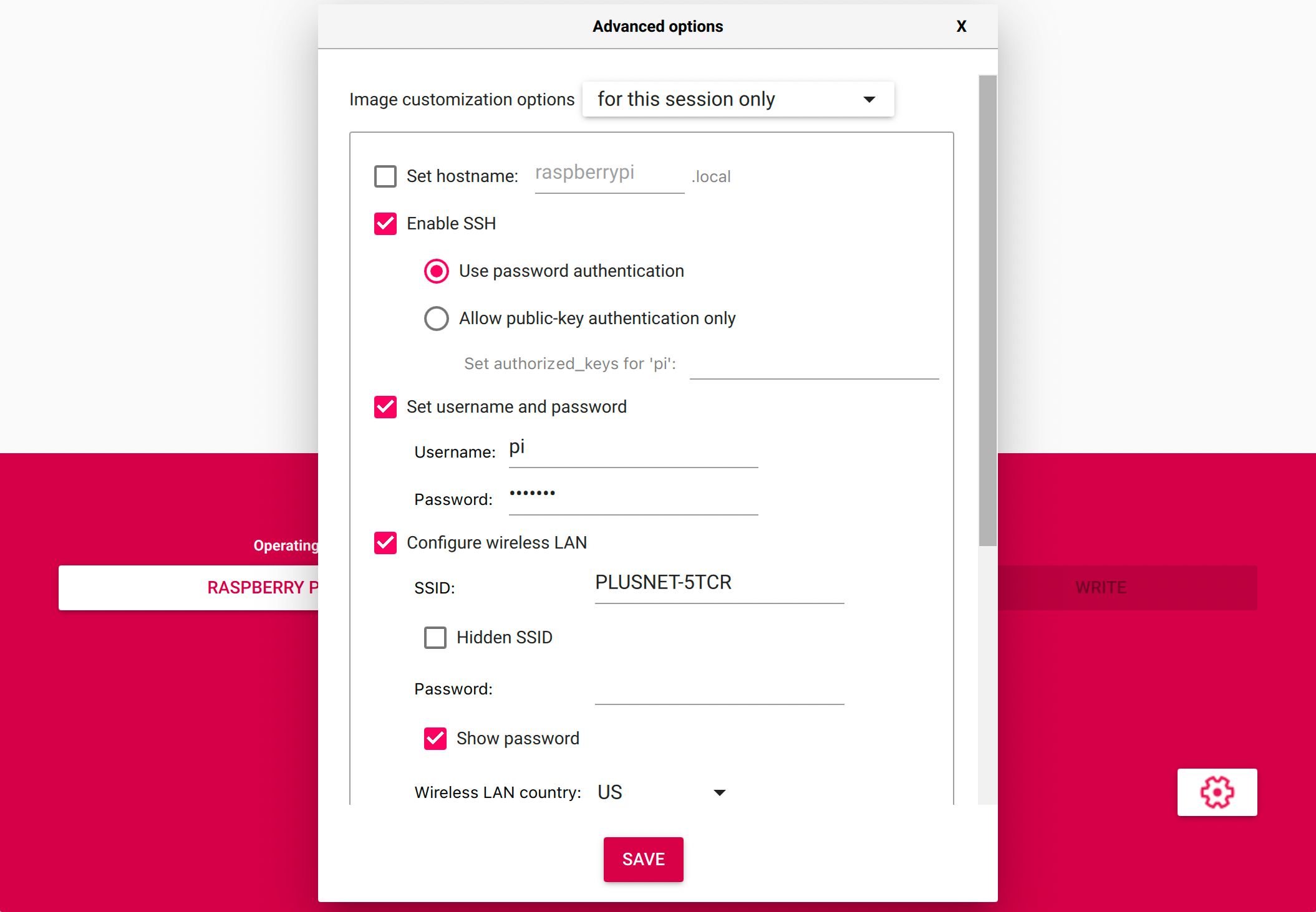
Security is, of course, of utmost importance, particularly when considering remote access. When implementing SSH, it is crucial to configure security measures to mitigate risks. Employing strong passwords or, preferably, key-based authentication is paramount. Regular password rotations and the implementation of multi-factor authentication (MFA) add an additional layer of security. Beyond these standard procedures, it is vital to ensure that SSH is configured to use the latest encryption protocols and that all devices are regularly patched with security updates. By prioritizing security, organizations can prevent unauthorized access, safeguard sensitive data, and maintain the integrity of their IoT deployments.
The versatility of "best remote SSH IoT" extends far beyond basic device management. It fuels the development and deployment of innovative solutions across various sectors. In smart agriculture, for instance, remote access allows farmers to monitor and control irrigation systems, environmental sensors, and other vital equipment from any location, empowering them to optimize resource utilization and increase yields. Within the healthcare industry, remote SSH access is pivotal for managing and maintaining medical devices in remote patient monitoring systems and healthcare facilities, leading to more efficient patient care and improved outcomes. In industrial automation, SSH offers a secure and reliable means to remotely control and monitor manufacturing equipment, increasing productivity and allowing for real-time adjustments. The benefits are clear: increased efficiency, enhanced security, and the capacity to unlock the true potential of IoT devices.
However, the selection and implementation of remote SSH solutions for IoT require careful consideration. The market offers a range of options, each with its own strengths and weaknesses. Factors such as the operating system of the IoT devices, the security requirements, and the available network infrastructure influence the suitability of a solution. Popular options include native SSH clients, which come pre-installed on many Linux-based devices, as well as more sophisticated solutions that offer advanced features such as centralized management, auditing, and access control. Moreover, considerations must extend to the network topology of the IoT deployment. The network infrastructure should support SSH connectivity and offer secure routes to remote devices. Firewalls, VPNs, and other security appliances must be configured correctly to allow the necessary traffic, while simultaneously protecting the devices from unwanted external threats.
The core strength of "best remote SSH IoT" is its adherence to industry standards. SSH is a widely accepted and thoroughly vetted protocol, ensuring that devices are interoperable and can be managed using existing infrastructure. This standardisation allows administrators to leverage a broad knowledge base and a vast array of tools to manage their deployments. Furthermore, the open-source nature of many SSH implementations enables customization and integration with existing systems, promoting flexibility and adaptability. From a management perspective, this ease of integration simplifies the ongoing maintenance and support of IoT solutions, reducing the costs associated with proprietary systems and vendor lock-in.
Looking ahead, the role of "best remote SSH IoT" is poised to become even more significant. As IoT technology continues to evolve, with the rise of 5G connectivity, edge computing, and advanced security measures, the demand for robust and secure remote access will only increase. Furthermore, advancements in automation and artificial intelligence are poised to drive the integration of remote SSH into sophisticated management systems, enabling automated diagnostics, proactive maintenance, and self-healing capabilities. The future of IoT will be driven by greater automation and intelligence, and "best remote SSH IoT" is fundamental to realising this vision.
In an era defined by constant technological progress, the ability to securely and efficiently manage and maintain IoT devices remotely is no longer a luxury; it is a necessity. By carefully considering the requirements of the deployment, selecting appropriate solutions, and implementing robust security measures, organizations can leverage "best remote SSH IoT" to enhance their operational efficiency, reduce costs, and unlock the full potential of their IoT deployments. The future is connected, and the key to unlocking its potential lies in the secure and intelligent management of the devices that drive it.
The benefits of leveraging best remote SSH IoT are multi-faceted and profound. They contribute significantly to the operational efficiency, security, and scalability of IoT deployments across all industries. Remote access allows administrators and developers to manage devices efficiently, cutting down on troubleshooting and maintenance time, thereby leading to a more productive and cost-effective operation. The deployment of strong security protocols, essential in protecting against unauthorized access, forms a cornerstone of responsible IoT implementation and fosters user trust in the technology. Finally, the capacity to manage a large number of devices, even across vast geographical areas, facilitates scalable solutions, which can evolve seamlessly with the growth of any organization.
Moreover, the adoption of "best remote SSH IoT" is not merely a technological decision; it is a strategic one that demonstrates a commitment to innovation and adaptability. It signals an understanding of the evolving technological landscape and a proactive approach to addressing its complexities. The companies and organizations embracing these practices will have a strategic edge, capable of responding quickly to challenges, adapting to new opportunities, and optimizing their IoT investments to maximum effect. The shift towards remote access is not merely a passing trend but a core element in the building of a flexible and resilient technological infrastructure.