Warning: 9,000+ VNC Endpoints Exposed! Security Risks & How To Protect Yourself
Is your remote access setup a ticking time bomb? The pervasive use of Virtual Network Computing (VNC) across diverse systems, combined with its often-neglected security, creates a fertile ground for cyberattacks, potentially exposing sensitive data and critical infrastructure.
The world of remote access, once a niche technology, has become an indispensable tool for businesses, individuals, and organizations of all sizes. Virtual Network Computing (VNC) stands as a prominent player in this landscape, offering a convenient means of controlling and viewing a computer remotely. However, behind its apparent simplicity lies a web of security vulnerabilities that demand serious attention. The inherent risks associated with VNC stem from its fundamental design and, critically, the often-lax security configurations employed by its users. This is not merely a technical concern; it is a significant threat to data integrity, privacy, and the overall stability of connected systems. The ease with which attackers can exploit these weaknesses underscores the urgent need for a comprehensive understanding of the threats and a proactive approach to securing VNC deployments.
At its core, VNC operates by transmitting a graphical representation of a computer's screen over a network. This, by itself, isn't inherently problematic. However, the traditional implementation of VNC, especially in its default configurations, presents several key security weaknesses. One of the most glaring issues is the unencrypted nature of its traffic. This means that the data being transmitted between the remote computer and the accessing device is not protected from eavesdropping. An attacker who intercepts this traffic can readily see everything displayed on the remote screen, including sensitive information like passwords, personal data, and confidential business documents. This inherent vulnerability makes VNC a prime target for man-in-the-middle attacks, where an attacker positions themselves between the user and the remote system to intercept and potentially manipulate the data flow.
Further compounding the problem is the often-weak authentication methods employed by VNC. Many VNC implementations rely on simple password-based authentication, which can be easily cracked using brute-force attacks or by leveraging compromised password databases. Moreover, the default passwords, or those set by users who may not fully grasp security best practices, are frequently easy to guess. This combination of unencrypted traffic and weak authentication creates a "perfect storm" for attackers, providing them with a straightforward path to gain unauthorized access to remote systems. The potential consequences of such breaches can be devastating, including data theft, system compromise, and even the deployment of ransomware or other malicious software. This is the reality of VNC's security weaknesses.
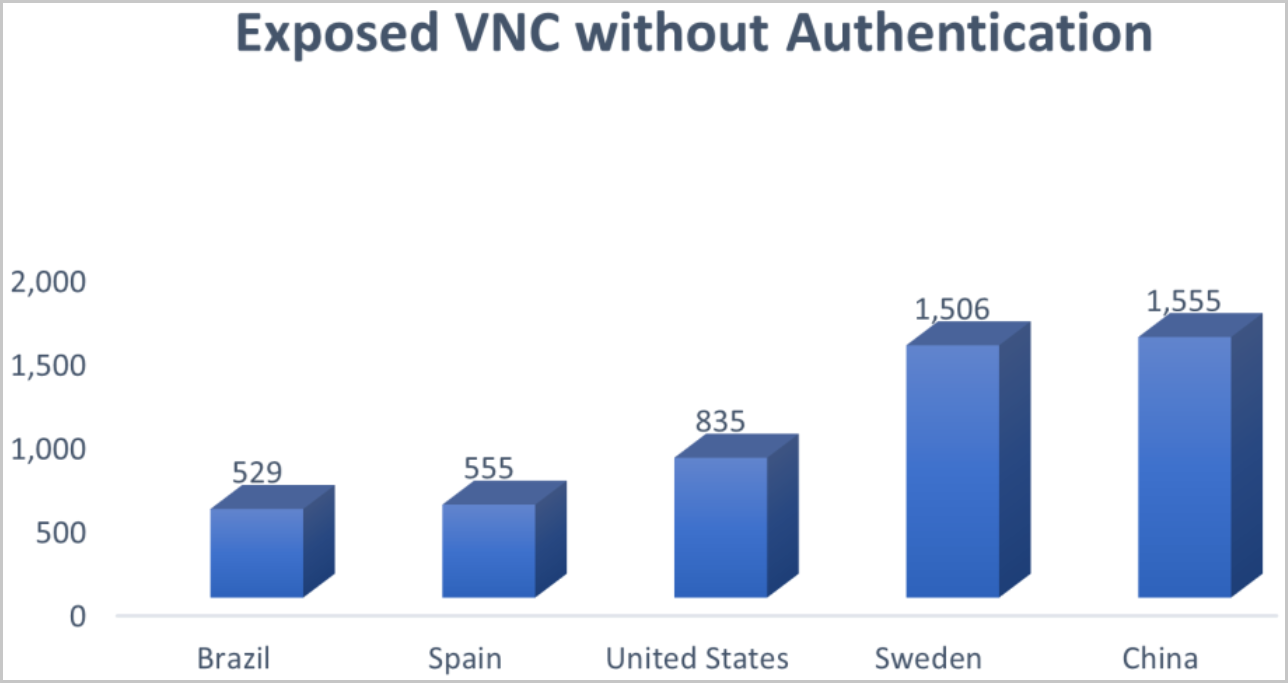
The scale of the problem is underscored by the sheer number of exposed VNC endpoints on the internet. According to recent findings from security researchers at Cyble, over 9,000 VNC endpoints were identified as being openly accessible, without any form of authentication. This means that anyone with an internet connection could potentially connect to these systems and gain access. This is a staggering figure that emphasizes the urgent need for improved security practices. The ubiquity of VNC and the ease with which it can be deployed also contribute to the problem. VNC is available for a wide range of operating systems and is often used as a convenience tool, which leads to it being deployed without proper security considerations.
Several specific vulnerabilities have been identified in various VNC implementations. Security researchers have cataloged a series of flaws that allows attackers to bypass authentication, execute arbitrary code, or escalate their privileges. The bleepingcomputer link, for example, lists a significant number of vulnerabilities across four VNC products. Some of these vulnerabilities are variations of those previously identified, indicating that the underlying security issues are persistent. In the case of UltraVNC, for example, over 20 security bugs have been identified. These examples demonstrate the ongoing challenges associated with securing VNC and the need for a continuous vigilance. The inherent complexity of these systems requires a strong understanding of security fundamentals and proactive measures.
VNC's reliance on specific network ports also adds another layer of risk. It commonly uses ports 5900 or 5800 to establish connections. This predictable port usage makes it easy for attackers to scan networks for vulnerable VNC instances. Once a vulnerable system is identified, the attacker can attempt to exploit any known vulnerabilities to gain access. The common use of these well-known ports also gives attackers a clear indication of what services are running on the targeted machine, giving them an additional advantage in mounting attacks. These vulnerabilities are very complex and needs to be addressed.
The security of VNC implementations varies depending on the specific software used. Some offer limited password strength options, while others try to enhance security by using SSH or VPN tunneling to encrypt traffic. However, even with these added features, the overall security posture is often dependent on the user's configuration and security awareness. The best practices should always be followed, and that is very important in this scenario.
The dangers of insecure VNC implementations are very real, and the potential impacts can be extensive. It should be approached cautiously and only implemented with robust security measures in place. Organizations and individuals must carefully assess their VNC deployments and make sure proper security practices are followed.
The security breaches have far-reaching consequences. Beyond the immediate risk of data theft, breaches can lead to reputational damage and financial losses. Organizations can be subject to regulatory penalties if sensitive data is compromised. The financial costs of recovering from an attack, including incident response, forensic investigations, and legal fees, can be substantial. The most damaging aspect of the breaches are the attacks on the organizations and the people connected with them.
Protecting against the security risks requires a layered approach. The first step involves strengthening the authentication mechanisms used by VNC. This includes using strong, unique passwords and enabling multi-factor authentication (MFA) where available. MFA adds an extra layer of security by requiring users to verify their identity through a second factor, such as a code sent to their phone, in addition to their password. Moreover, security experts recommend that all VNC traffic should be encrypted. Using SSH or VPN tunnelling provides end-to-end encryption, protecting the data from interception. This ensures that the communication is protected against attackers.
It is crucial to keep the software up to date and follow the recommended security configuration. The software vendors are always releasing updates to patch known vulnerabilities. It is very important to ensure the latest version is installed and the configuration of each VNC installation is secure.
Access controls should be very important in securing VNC deployments. Implementing strict access controls limits the number of users who can connect remotely. This minimizes the attack surface and reduces the potential for unauthorized access. This ensures only authorized people have access. By enforcing strict access controls, organizations can limit the scope of potential breaches and reduce the risk of sensitive information falling into the wrong hands. These measures are essential for building a robust security posture. Limiting access rights to only those individuals who absolutely need remote access reduces the attack surface.
Organizations must also implement network segmentation. This means segmenting the network into different zones, separating sensitive systems from less critical ones. This helps to contain any potential breaches. If an attacker manages to compromise a VNC instance, they are contained within the segmented zone, preventing them from moving laterally across the entire network. This makes it much harder for attackers to gain access. This minimizes the impact of security breaches. If the attackers can't move laterally then the security will be less impacted and the risk can be reduced. Implementing network segmentation should be considered as one of the key factors.
Regular security audits and penetration testing are also essential. These processes help to identify vulnerabilities in VNC deployments and uncover any misconfigurations that could leave systems vulnerable. Regular security audits involve a comprehensive review of the security posture, assessing security controls, configurations, and compliance with industry best practices. Penetration testing, also known as ethical hacking, simulates real-world attacks to identify vulnerabilities and weaknesses. This proactive approach helps organizations identify and address potential risks before they can be exploited by malicious actors. This helps with identifying security gaps and it is essential for ensuring the ongoing security of VNC deployments.
In conclusion, the security weaknesses in VNC are a genuine concern. The pervasive use of the technology, coupled with its inherent vulnerabilities, creates significant risks for organizations and individuals. By implementing best practices, including strong authentication, traffic encryption, regular patching, access controls, and network segmentation, it is possible to mitigate these risks. The adoption of robust security measures will require a shift in mindset from convenience to security, ensuring that remote access is provided without compromising security. Only through this proactive and comprehensive approach can we hope to reduce the risk of VNC-related security breaches and safeguard valuable data and systems.